Imagine buying a smartphone that crashes every time you open an app—frustrating, right? Now, picture one that runs smoothly, day after day, without a hitch. That is the clear answer to the question, “What is Quality Assurance (QA) all about?”
At its core, QA is a systematic process designed to ensure that products or services meet specific standards and fulfill customer expectations. It’s the unsung hero behind the reliability we often take for granted, from the cars we drive to the software we use.
In this article, we’ll dive into what quality assurance means, why it’s so vital in today’s world, how it works behind the scenes, and where it’s headed in the future. Whether you’re a business owner, a professional, or simply curious, understanding QA can shed light on why some things succeed while others fail.
What is quality assurance?
QA - Quality Assurance is a proactive, process-driven approach to prevent defects before they happen. Unlike Quality Control (QC), which inspects finished products to catch flaws, QA focuses on building quality into every step of creation.
You can think of QA as the architect designing a sturdy house, while QC is the inspector checking for cracks after it’s built.
However, the concept of quality assurance has evolved. It began in the industrial age when manufacturers ensured goods met basic standards. Since then, it has expanded into fields like software development, healthcare, and hospitality.
At its heart, quality assurance (QA) rests on a few key principles: preventing issues rather than fixing them and striving for continuous improvement. Additionally, quality assurance is also about keeping the customer’s needs front and center and standardizing processes to ensure consistency.
Today, QA touches nearly every industry, making it a universal backbone of excellence.
The importance of quality assurance in software testing
Now that we’ve answered the question “What is quality assurance?”, the next one is: Why does QA matter?
Simple: it’s the difference between a product you trust and one you regret buying. Quality assurance ensures that what you deliver—a car, an app, or a medical device—is consistent and reliable. This consistency builds customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are gold in any market.
Beyond happy customers, QA reduces risks. A software company that skips QA might release a buggy update, losing users and revenue. A car manufacturer ignoring QA could face a costly recall—or even worse, endanger lives.
There are some real-world examples that abound: Toyota’s reputation for reliability owes much to rigorous QA, while software flops like the 2013 Healthcare.gov launch show what happens when QA falls short.
QA also saves money by catching issues early, before they spiral into expensive fixes. In competitive industries, it’s a differentiator—brands known for quality stand out.
Plus, in regulated fields like healthcare, QA ensures compliance with strict standards, protecting both companies and consumers. In short, QA isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a must for trust, safety, and success.
How quality assurance works
So, how does QA actually get the job done? Let’s break it down.
1. The QA Workflow
QA follows a clear, step-by-step approach:
- Step 1: Establish quality benchmarks and criteria. This means setting clear goals, like product specifications or legal regulations, to define “good enough.”
- Step 2: Create systems and guidelines. Teams design processes—like coding standards for software or assembly protocols for manufacturing—to hit those targets.
- Step 3: Track and assess progress. Throughout development or production, QA monitors how things are going, using data and observation.
- Step 4: Spot and fix potential problems. If something’s off—like a glitchy feature or a weak part—QA steps in before it’s too late.
- Step 5: Evaluate results and tweak processes. After launch or delivery, feedback drives refinements to make the next round even better.
2. QA Methods and Tools
QA relies on a toolbox of techniques:
- Inspections and evaluations. Internal audits or third-party reviews check that standards are met.
- Testing approaches. Software gets unit tests to catch bugs; manufactured goods face durability trials.
- Data-driven monitoring. Tools like Statistical Process Control (SPC) use numbers to spot trends.
- Risk assessment strategies. Teams predict where failures might occur and plan ahead.
- Record-keeping. Quality handbooks and standard operating procedures (SOPs) keep everyone on the same page.
3. Who’s Involved in QA
QA isn’t a solo act. Specialists—think testers, auditors, or engineers—lead the charge, ensuring processes stay on track. But they don’t work alone.
In software, they collaborate with developers; in manufacturing, with production crews; in services, with frontline staff. Leadership plays a big role, too—without their support, QA lacks teeth.
Additionally, training everyone involved ensures the whole team understands and values quality, making QA a company-wide effort.
What are the quality assurance methods?
Quality Assurance (QA) relies on a variety of proven strategies to ensure products and services consistently hit the mark. Here are some standout methods that businesses use to maintain excellence.
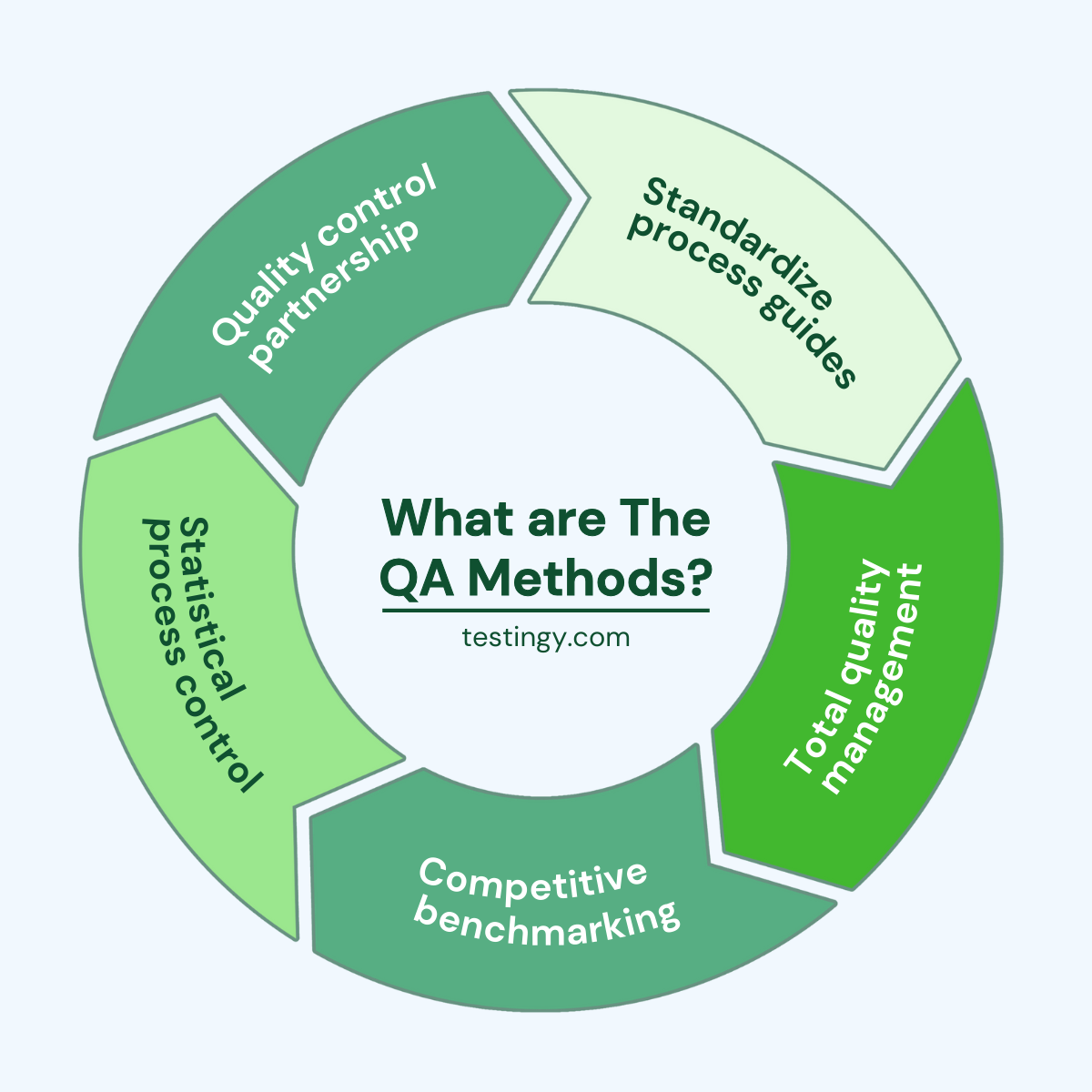
1. Standardized process guides
A strong QA foundation starts with clear, written instructions. By documenting procedures, guidelines, and expectations, companies create a roadmap everyone can follow.
As a result, this keeps teams aligned and serves as a yardstick for spotting where things can improve, ensuring quality stays on track from start to finish.
2. Total quality management (TQM)
TQM is a full-team commitment to quality, from the CEO to the shop floor. It’s about constantly refining every process, whether production or customer support, to eliminate waste and boost efficiency. With everyone pitching in, TQM turns quality into a company-wide mission, not just a checklist.
3. Competitive benchmarking
Why reinvent the wheel when you can learn from the best? Benchmarking pits your processes against industry leaders, revealing gaps and sparking ideas for improvement. By adopting top-tier practices, businesses can elevate their standards and stay ahead of the curve.
4. Statistical process control (SPC)
Numbers don’t lie, and SPC uses them to keep quality in check. By tracking real-time data, this method spots trends or hiccups before they become defects. Some quality assurance tools can help teams tweak processes on the fly, ensuring consistent results without the guesswork.
5. Quality control partnership
QA doesn’t work alone—it teams up with Quality Control (QC) for a one-two punch. While QA builds the systems to prevent issues, QC jumps in with inspections and tests to catch anything that slips through. Together, they form a tight net, ensuring nothing subpar reaches the customer.
Benefits and challenges of quality assurance
QA isn’t just a process for the sake of process—it delivers real value, though it’s not without hurdles.
Benefits:
- Customer satisfaction. Reliable products keep people coming back.
- Cost savings. Fixing a flaw early is cheaper than recalling a million units.
- Competitive edge. Quality stands out in crowded markets—think Apple’s polished tech.
- Credibility. A strong QA track record builds trust with customers and regulators.
Challenges:
- Upfront costs. Training, tools, and time add up before benefits kick in.
- Resistance. Teams that got used to “good enough” might push back on stricter processes.
- Speed vs. quality. In fast-moving fields like tech, QA can feel like a bottleneck.
- Adaptation. Keeping up with new tech and standards takes effort.
The future of quality assurance
QA isn’t static—it’s evolving with the world. Automation and AI are game-changers: machine learning can predict defects before they happen, and automated testing tools run checks faster than humans ever could. In software, DevOps is blending QA into continuous development cycles, making quality a nonstop priority.
Besides, sustainability is another frontier. QA now ensures eco-friendly practices—like verifying a product’s carbon footprint—alongside traditional metrics. As tech like the Internet of Things (IoT) and quantum computing emerges, QA will adapt to smarter test management with interconnected systems.
In a digital, global economy, QA’s role is growing. Customers demand perfection, and companies can’t afford slip-ups. Will AI replace human QA? More likely, it’ll enhance it, freeing people to focus on strategy while machines handle the grunt work. The future of QA is dynamic, tech-driven, and more critical than ever.
Conclusion on what is quality assurance
Quality Assurance is the backbone of excellence, weaving reliability into every step from design to delivery. It’s about preventing headaches, ensuring consistency, and earning trust—whether you’re building a skyscraper or an app. For businesses, it’s a smart investment; for customers, it’s a silent promise of quality.
So, you can thank QA the next time you enjoy a seamless product or service. Businesses should prioritize it, and we should all appreciate its quiet impact. After all, Quality Assurance isn’t just a process—it’s a promise of reliability in an unpredictable world.
And don’t forget to check out Testingy - your next-gen test management tool to optimize your testing cycles and QA processes.