Automated testing allows development teams to verify software functionality quickly and consistently. As release cycles accelerate and applications become more complex, implementing effective test automation has become critical for maintaining quality while meeting deadlines.
What is Automated Testing?
Automated testing is the process of using software tools to execute test cases automatically, reducing the need for manual effort.
Unlike manual testing, where a tester interacts with the application step by step, automated testing runs pre-written scripts that simulate user actions, check system responses, and verify expected outcomes. This makes it faster, more consistent, and ideal for repetitive or large-scale testing.
In modern software development, automated testing plays a crucial role in Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD). Whenever developers push new code, automated tests run immediately to catch potential bugs before the software moves to production. This ensures faster releases while maintaining high quality, making automation a key part of Agile and DevOps workflows.
What is the main purpose of automated testing?
The main goal of automated testing is to increase efficiency, improve software quality, and speed up development cycles. By automating repetitive test cases, teams can quickly detect bugs, verify functionality, and ensure that software works as expected across different environments.
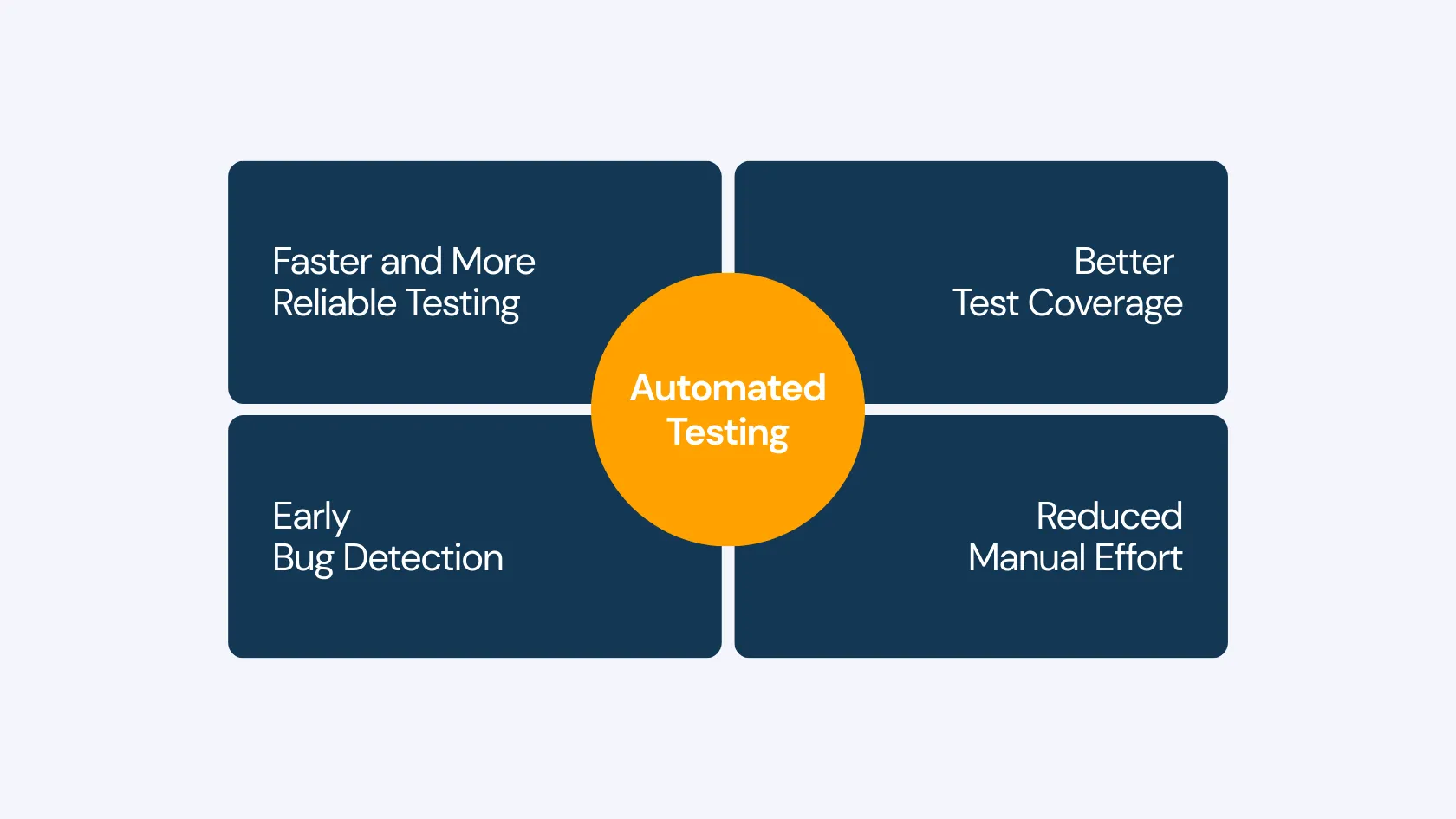
Here’s why automated testing is essential:
- Faster and More Reliable Testing: Automated tests run quickly and consistently, reducing the risk of human errors.
- Better Test Coverage: It allows for testing across multiple devices, platforms, and scenarios that would be time-consuming manually.
- Early Bug Detection: Running tests frequently helps catch defects early, making them easier and cheaper to fix.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automating repetitive tasks frees up testers to focus on more complex and exploratory testing.
While automation speeds up testing and enhances accuracy, it doesn’t completely replace manual testing. Instead, it works best when combined with manual efforts to ensure a well-rounded and effective testing strategy.
Manual vs. automated testing
Manual testing and automated testing serve different purposes in software development. Below is a comparison of the key differences:
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Automated Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Testers manually perform test cases step by step | Tests run automatically using scripts and testing tools |
| Speed | Slower due to manual effort and human limitations | Much faster, allowing multiple tests to run simultaneously |
| Reliability | Prone to human errors and inconsistencies | Highly consistent and repeatable with minimal errors |
| Cost | Lower initial costs but higher ongoing labor costs | Higher upfront costs but more cost-effective over time |
| Test Coverage | Limited due to time and effort constraints | Broader coverage, enabling large-scale and repeated testing |
| Best Use Cases | Exploratory, UI/UX, one-time tests, and new features | Regression, performance, and frequent repetitive tests |
| Maintenance | Easier to adjust test cases but time-consuming for large projects | Requires effort to create scripts but is easier to maintain long-term |
| Feedback Speed | Slower since tests take longer to execute and analyze | Faster feedback, enabling quicker development cycles |
Both methods are essential in software testing. Manual testing is best for exploratory and usability testing, while automated testing is crucial for efficiency, accuracy, and handling large test suites. Many teams use a mix of both approaches to achieve optimal software quality.
Why should you transition from manual to automated testing?
Transitioning to automated testing helps teams work faster and more efficiently. Manual testing is valuable but time-consuming and prone to human error. Automation ensures consistency, speeds up test execution, and reduces repetitive manual work.
With automated testing, teams get faster feedback, detect bugs early, and scale testing across different environments. This leads to quicker releases and higher software quality without increasing manual effort.
Test automation vs. Automated testing: What’s the Difference?
Test automation and automated testing are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same.
Test automation refers to the broader process of using tools, scripts, and frameworks to automate various testing activities, such as test execution, reporting, and environment setup. It is a strategy to improve efficiency in the testing lifecycle.
Automated testing, on the other hand, is the specific practice of running test cases automatically instead of manually. It is a part of test automation, focusing on executing predefined tests using automation tools.
While automated testing ensures that software functions as expected, test automation streamlines the entire testing workflow, making continuous testing possible in modern development.
Types of automated testing
Not all tests benefit from automation, but certain types are ideal due to their repetitive nature and need for accuracy.
- Unit Testing: Focuses on verifying the functionality of individual components or modules in isolation. By testing each part separately, developers can identify and fix issues early in the development cycle.
- Integration Testing: Assesses the interaction between integrated modules or components to ensure they work together as intended. This type of testing helps detect interface defects between modules.
- Functional Testing: Evaluates the software against its functional requirements, ensuring that each feature operates in accordance with the specified criteria. This testing validates the system's actions and outputs.
- Regression Testing: Involves re-running previously conducted tests to confirm that recent code changes have not adversely affected existing functionalities. It ensures that new developments do not introduce new bugs.
- Performance Testing: Measures the software's responsiveness, stability, and scalability under various conditions. This includes load testing, stress testing, and assessing the system's behavior under peak loads.
While automation improves efficiency, not all tests should be automated.
Popular test automation tools and frameworks
Effective test automation relies on both a good structure (framework) and the right software (tools). Frameworks organize your test scripts, improving efficiency and maintainability, while tools are used to write and execute those scripts.
Understanding Framework Structures:
Here are three foundational approaches to structuring test automation:
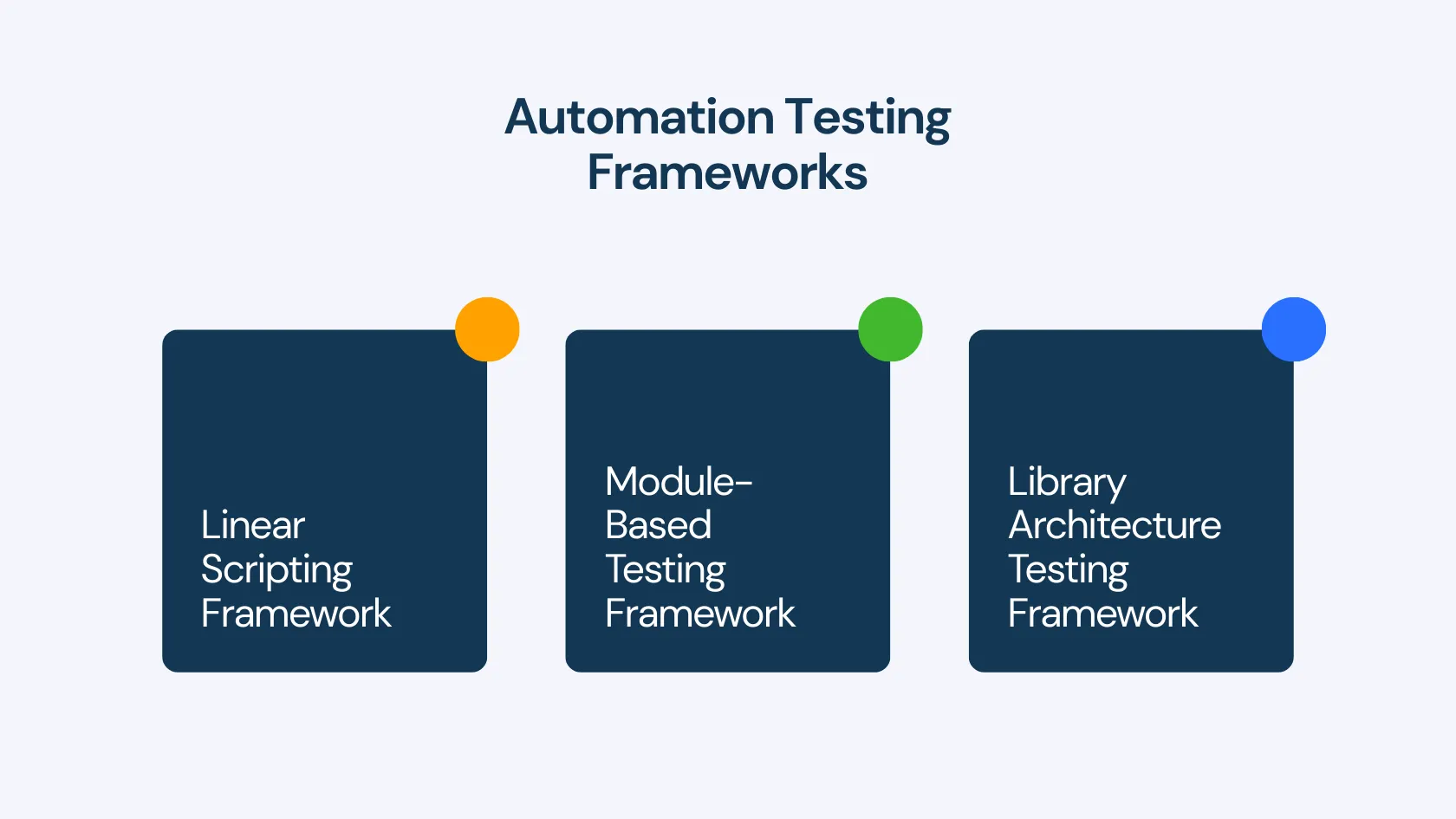
- Linear Automation Framework: Also known as the Record and Playback framework, this approach involves recording each step performed by the tester and playing it back to conduct the test. It's straightforward but can be less scalable for complex applications.
- Modular-Based Testing Framework: This framework divides the application under test into separate modules, each tested independently. Test scripts for each module are created and then combined to build larger test scenarios, promoting reusability and maintainability.
- Library Architecture Testing Framework: Similar to the modular framework, this approach groups common tasks into functions, which are then stored in a library. Test scripts can call these functions, enhancing code reusability and reducing maintenance efforts.
Common Automation Tools:
While frameworks provide the structure, these popular tools help implement and run your automated tests:
- Selenium: A widely-used, open-source standard for automating web browser interactions, supporting multiple programming languages.
- Cypress: A modern, JavaScript-based framework for faster and more reliable end-to-end web testing.
- Playwright: An open-source tool from Microsoft offering robust end-to-end testing across major web browsers (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit).
- Appium: An open-source standard for automating tests on mobile applications (native, hybrid, mobile web) across iOS and Android.
Choosing the right combination of framework principles and tools depends on your project's complexity, the type of application being tested (web, mobile), and your team's technical skills.
Final Thoughts
Automated testing reduces manual effort, increases test coverage, and provides faster feedback, allowing teams to deliver better software more quickly.
For best results, prioritize automating tests that run frequently or cover critical functionality. Begin with a small set of automated tests and expand gradually as your team builds expertise with Testingy.